I’ve faced survival challenges that took away all comforts. I learned a harsh truth: food security is not a luxury, it’s essential. Your ability to find sustainable food could be the difference between life and death.
Between 1960 and 2000, farming innovations changed how we grow food. In countries like Mexico and India, crop yields soared thanks to science. These advances are not just history; they’re survival strategies for food security.
Key Takeaways: Sustainable Food Sources
- Sustainable food sources are critical for long-term survival
- Organic farming techniques provide flexible nutrition strategies
- Diversifying food sources increases survival chances
- Local food systems offer immediate nutrition solutions
- Agricultural innovation is key to food security
Local food systems have grown from simple practices to advanced survival methods. Learning about sustainable food sources is more than just growing crops. It’s about creating strong nutrition plans that work when usual food chains fail.
Building Self-Sufficient Food Systems
Food security is key to survival, more so in uncertain times. Learning to create sustainable food sources changes how we view nutrition and self-reliance. Our modern farming needs new, innovative methods beyond old ways.
The U.S. is seeing big changes in farming. New tools in precision agriculture are saving 100 million gallons of fuel and cutting herbicide use by over 30 million pounds.
Understanding Food Security Basics
Food security means more than just having food. It’s about building strong systems that can face environmental challenges. Urban farming and local agriculture are key to sustainable food plans.
- Develop diverse crop selection
- Implement permaculture principles
- Create backup food preservation methods
Developing Long-Term Food Strategies
Planning for food long-term means knowing about environmental impacts and sustainable practices. The farming world is working hard to lessen its ecological footprint.
| Sustainability Goal | Target | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Greenhouse Gas Reduction | 10% by 2025 | U.S. Soy Industry Initiative |
| Soil Organic Matter | 16% Return | Anuvia Plant Nutrients |
Creating Renewable Food Sources
Renewable food sources are vital for long-term survival. Permaculture brings new ways to make sustainable food systems that blend with nature.
“The future of food security lies in understanding and working with nature, not against it.” – Sustainable Agriculture Expert
By using urban farming, local agriculture, and new farming tech, people can build strong food security networks. These networks offer nutrition and resilience in tough times.
Sustainable Food Sources: Essential Components
Sustainable food production is not just a trend; it’s crucial for our survival. Regenerative agriculture is a key strategy to change our food systems. It aims to improve ecosystem health while making food nutritious.
“The future of food depends on our ability to work with nature, not against it.” – Sustainable Agriculture Expert
Agroecology offers a complete view of food production. It combines ecological principles with farming practices. This way, we can build stronger and more productive food systems.
- Reduce food waste through strategic planning
- Implement plant-based diet alternatives
- Support local food production networks
- Prioritize seasonal and organic ingredients
Local food has amazing benefits. Studies show that locally grown foods:
- Keep more nutrients
- Lower carbon emissions
- Boost community economies
- Encourage sustainable farming
More than 70% of global freshwater is used for farming. This highlights the need for sustainable food systems. Switching to more ecological methods can greatly reduce harm to the environment.
Plant-based diets are a strong solution. They help lower carbon emissions and support global food security. By eating less meat, we can make a big difference.
Raising Livestock for Protein Security
Livestock farming is key for survival and self-sufficiency. The world is facing big challenges in feeding more people. This is because food production is changing fast.
By 2050, we’ll need twice as much meat as we did in 2012. This makes breeding animals in a sustainable way very important. Learning about managing livestock can help you become more food independent.
Chicken Farming Fundamentals
Chicken farming is a good start for making protein. Here are some important points:
- Minimal space requirements
- Rapid reproduction cycles
- Lower initial investment compared to larger livestock
- Multiple product streams (meat and egg production)
Egg Production Management
Good egg production needs careful planning. Sustainable egg production is more than just collecting eggs. It’s about creating a healthy environment for chickens.
“Every chicken is a potential protein generator for your survival strategy.”
Sustainable Breeding Practices
Sustainable breeding is about quality, not just quantity. The United Nations suggests improving animal welfare. They recommend the ‘Five Freedoms’ framework.
- Genetic diversity preservation
- Disease-resistant breeding
- Efficient feed conversion
- Stress reduction techniques
By using agroforestry and ethical breeding, you can make a strong protein source. This supports both human health and the environment.
Growing Your Own Fruit Trees and Orchards
Starting your own fruit trees turns your yard into a place where you can grow food. Using agroforestry, you make a strong ecosystem that feeds you and helps with food security for a long time. Picking the right fruit trees is key for a good orchard.
When planning your fruit tree setup, keep these tips in mind:
- Choose varieties that fit your local weather
- Put different fruit tree species together
- Think about the different spots in your orchard
- Use permaculture to keep the ecosystem balanced
Permaculture principles really help your orchard grow. By copying nature, you make a place where fruit trees do well. Even small city areas can have fruit trees, making food easy to get for all.
“A well-designed orchard is not just a food source, but a living, breathing ecosystem.” – Sustainable Agriculture Expert
To grow fruit trees well, you need to know about the soil, feeding them right, and planting smart. Begin with a soil test, pick organic food for your trees, and let them grow slowly. Your hard work will pay off with healthy food for many years.
Root Vegetables: The Foundation of Food Independence
Food independence starts underground. Root vegetables are key, offering vital nutrients and great storage. They help families get through tough times.
Choosing the right crops makes root vegetables a strong survival plan. These crops are full of nutrients and help ensure food security for a long time.
Best Root Crops for Survival
- Potatoes: High-calorie, versatile crop with extended storage potential
- Carrots: Rich in vitamins, adaptable to various growing conditions
- Onions: Natural preservation properties, long shelf life
- Beets: Nutrient-dense, excellent for root crop storage
- Jerusalem artichokes: Drought-resistant, high-yield vegetable
Storage and Preservation Techniques
Keeping crops stored right is key to food independence. Old ways of preserving root vegetables keep them fresh for months.
| Preservation Method | Storage Duration | Best Crops |
|---|---|---|
| Root Cellar Storage | 3-6 months | Potatoes, Carrots, Beets |
| Dehydration | 1-2 years | All root vegetables |
| Fermentation | 6-12 months | Beets, Carrots |
Year-Round Growing Techniques
To grow root vegetables all year, you need a plan. Succession planting and greenhouses help keep crops coming.
“In survival, your garden is your lifeline. Root vegetables are your insurance policy against hunger.” – Survival Agriculture Expert
The American Farmland Trust backs sustainable farming. They say diverse crops are crucial for food safety. Learning to grow root vegetables builds resilience.
Wild Food Foraging Strategies
Wild food foraging is key for living sustainably and having control over our food. Our ancestors knew how to find food in nature. Today, we can still learn from them and live more self-sufficiently.
To forage well, you need more than just to walk in the woods. You must know your plants, respect nature, and understand how to find food in it.
“Nature provides, but only for those who know how to listen and observe.” – Traditional Forager Wisdom
Essential Foraging Principles
- Identify plants with 100% certainty before harvesting
- Practice sustainable harvesting by taking only 10% of available plants
- Avoid foraging near polluted areas like roadsides
- Always obtain permission when foraging on private property
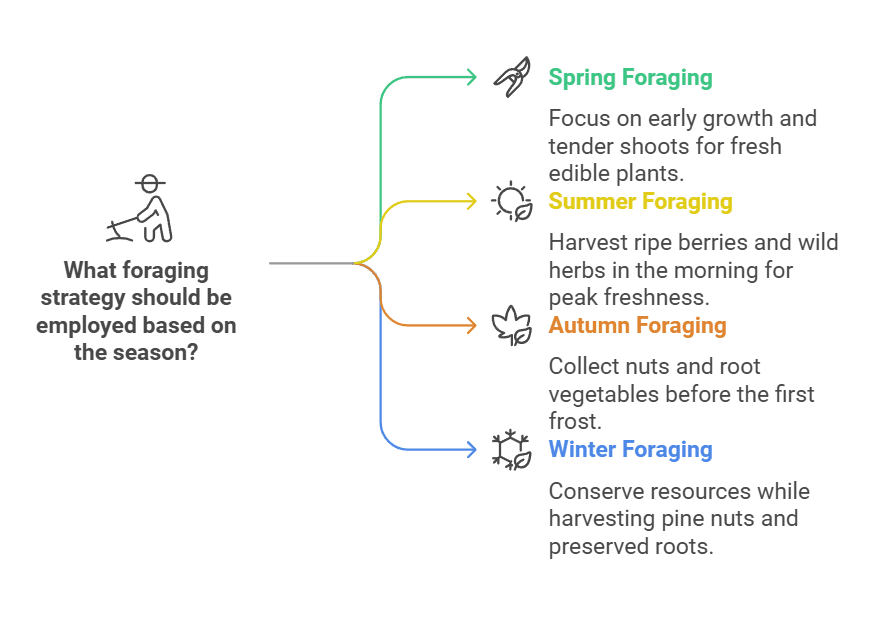
Seasonal Foraging Strategies
| Season | Recommended Edible Plants | Harvesting Tips |
|---|---|---|
| Spring | Dandelions, Ramps, Nettles | Early growth, tender shoots |
| Summer | Berries, Wild Herbs, Mushrooms | Peak ripeness, morning harvest |
| Autumn | Nuts, Late Berries, Root Vegetables | Before first frost, careful selection |
| Winter | Pine Nuts, Bark, Preserved Roots | Minimal harvesting, conservation focus |
Knowing how to harvest sustainably means understanding plant cycles. Ethical foragers make sure plants can grow back. This keeps our food and environment healthy.
Today, we have tools like foraging apps to help us learn. These apps can tell us which plants are safe to eat. Always be careful and don’t eat something you’re not sure about.
Hunting and Wildlife Management
Hunting is a key skill in sustainable food systems. It connects us directly with nature’s food. It’s more than just getting food; it’s about keeping nature in balance and using resources wisely.
Sustainable hunting is vital for wildlife conservation. The Pittman-Robertson Act shows this by giving over $1.1 billion for conservation projects in the U.S. in 2023.
Seasonal Hunting Guidelines
Good hunting needs planning and following rules. Hunters must think about a few important things:
- Respect seasonal hunting times
- Know about local wildlife numbers
- Get the right licenses and permits
- Follow bag limits and rules for each species
Game Processing and Storage
Properly processing game meat makes it more nutritious. Important steps include:
- Field dress right after hunting
- Cool meat quickly
- Use careful butchering methods
- Package well for long storage
Sustainable Wildlife Population Management
Wildlife management is a complex science. It uses many strategies:
| Management Strategy | Primary Objective |
|---|---|
| Controlled Hunts | Prevent Overpopulation |
| Habitat Restoration | Maintain Ecosystem Balance |
| Remote Sensing Technologies | Monitor Wildlife Habitats |
“Hunting is not just about harvesting animals, but understanding and preserving our natural ecosystems.” – Wildlife Conservation Expert
By using science, conservation, and responsible hunting, we can keep wildlife populations healthy. This ensures food for our communities.
Permaculture Practices for Long-Term Sustainability
Permaculture is a new way to farm that changes how we design food systems. It was started in the 1970s by Bill Mollison and David Holmgren in Australia. This method creates ecosystems that work together and are self-sustaining.
“Permaculture is not just about growing food, but about designing resilient systems that work with nature, not against it.”
Permaculture has three main ethics: People Care, Earth Care, and Fair Share. These guide farmers to make systems that are good for both the planet and people.
- Observe and interact with natural landscapes
- Catch and store renewable energy
- Obtain sustainable yields
- Practice self-regulation
- Value diversity in ecosystem design
Using permaculture practices can be done in many ways. It can be in small gardens or big farms. The goal is to understand how all parts work together.
| Permaculture Zone | Primary Focus |
|---|---|
| Zone 0 | Home and personal living space |
| Zone 1 | Intensively managed kitchen garden |
| Zone 2-3 | Crop production and food forests |
| Zone 4-5 | Wild harvest and forest management |
Permaculture uses agroecology to make food systems strong. These systems need less outside help and work better with nature. This is good for gardens and big farms alike, helping us have food for a long time.
The great thing about permaculture is how it can be used. It works in cities and in the countryside. It can be changed to fit different places and needs.
Conclusion
Achieving food security needs a careful and wide-ranging plan. Our study shows key insights into lasting food sources. These can greatly improve our survival chances.
With 5,285 adults studied, we learned how important it is to care for our planet. Making smart food choices is crucial for our health and the planet’s.
Being self-sufficient is now a must in our uncertain world. The study found that eating healthily and sustainably greatly affects our food choices. It shows we can boost our food security by choosing better farming methods and eating mindfully.
Industrial farming is a big problem, using over 70% of the world’s water and causing a lot of pollution. By choosing organic farming, permaculture, and buying local, we can build strong food systems. These systems protect our health and the planet’s.
Your journey to food independence begins with learning, adapting, and taking action. Whether it’s raising animals, growing food, or using new farming methods, each step gets you closer to a safer and greener future. It’s time to start – your future depends on it.
FAQ: Sustainable Food Sources – Grow and Hunt for Long-Term Survival
When it comes to long-term survival, the key lies in sustainable food sources. Growing and hunting your own food ensures a secure food supply while promoting environmental sustainability.
Below, we tackle your most pressing questions about sustainable diets, food production, and sustainable choices for survival, all written in the engaging style of Clayton Makepeace.
1. What Is a Sustainable Diet, and Why Is It Important for Survival?
A sustainable diet minimizes environmental impact while providing adequate nutrition for long-term survival. It focuses on using environmentally-friendly foods, such as locally grown plant foods, sustainably sourced animal proteins, and climate-friendly food options.
By adopting a sustainable diet, you not only secure your food supply but also align with sustainable values, reducing your overall foodprint (your personal impact on the global food systems).
2. What Are the Basics of Sustainable Food Production?
Sustainable food production involves using environmentally sound food production practices that maintain soil health, conserve water, and minimize harmful emissions. This includes:
- Organic Farming: Organic farmers rely on natural fertilizers and avoid harmful food additives to produce fresher foods with a lower environmental impact.
- Sustainable Farming Practices: These include crop rotation, permaculture, and using sustainable ingredients like heirloom seeds and drought-resistant plants.
The goal is to create a food production system that supports a sustainable food future while reducing food miles—the distance food travels from farm to table.
3. How Can I Secure a Long-Term Food Supply?
Securing a sustainable food supply involves both growing your own food and hunting responsibly. Here are some tips:
- Grow Your Own Food: Focus on high-yield, nutrient-dense plants such as beans, leafy greens, and root vegetables. These are staples of a sustainable foods list.
- Hunt and Forage: Incorporate sustainable hunting and foraging practices. Stick to game populations that are abundant and avoid overharvesting wild plants.
- Preserve Your Harvest: Learn food preservation techniques like drying, canning, and fermenting to maintain a nutritional food supply year-round.
These methods not only ensure food security but also reduce dependence on traditional food manufacturers.
4. What Are the Best Sustainable Food Options for Survival?
Sustainable food choices vary depending on your environment and dietary needs. Here’s a breakdown of sustainable food options:
- Plant-Based Diets: Vegetarian diets and vegan-friendly foods, such as legumes, grains, and nuts, are excellent for reducing your foodprint and conserving resources.
- Hunted Game: Wild-caught meats provide a high-protein, sustainable alternative to factory-farmed options.
- Sustainable Ingredients: Foods like heirloom vegetables, native plants, and climate-friendly food crops like quinoa and millet are ideal for survival situations.
Choosing from a sustainable foods list helps ensure a secure food supply that aligns with nutrition source sustainability.
5. How Does Hunting Fit into Environmental Sustainability?
Hunting, when done responsibly, is a sustainable alternative to relying on the industrial food industry. It helps control animal populations, reduces your dependence on food manufacturers, and provides a clean, organic protein source. Key principles include:
- Sustainable Use: Only harvest what you need to avoid depleting wildlife populations.
- Minimal Waste: Use as much of the animal as possible, from meat to hides, to honor the principle of sustainable development.
- Regulation Compliance: Follow local hunting regulations to maintain the balance of the food production landscape.
6. What Role Does Food Preservation Play in a Survival Plan?
Food preservation is essential for creating a sustainable food future. It allows you to store fresher foods and maintain their nutritional value for longer periods. Methods include:
- Canning: Ideal for preserving fruits, vegetables, and even hunted meats.
- Drying: A lightweight option for long-term storage of plant food and proteins.
- Freezing: If you have access to energy, freezing is a great food transformation technique to ensure freshness.
These practices reduce your reliance on the global food systems and support a secure food supply.
7. How Do Food Miles Impact Environmental Sustainability?
Food miles measure the distance food travels from production to your plate. Reducing food miles is critical to achieving sustainable food development. Here’s how you can minimize your impact:
- Grow your own food to eliminate transportation entirely.
- Support local organic farmers to cut down on international food additives and transportation emissions.
- Choose sustainably food products that are grown or produced in your region.
Fewer food miles mean a smaller carbon footprint and more sustainable food choices.
8. Can a Sustainable Diet Include Different Foods Like Meat and Plant-Based Options?
Absolutely! A balanced sustainable diet includes a variety of different foods. For example:
- Plant-Based Foods: Fruits, vegetables, grains, and legumes are staples of any sustainable food development strategy.
- Animal-Based Foods: When sourced sustainably, meats from hunted game or responsibly raised livestock are excellent protein sources.
The key is balancing your food production practices to ensure a sustainable food future while meeting your dietary needs.
9. What Is the “Great Food Transformation,” and How Does It Relate to Survival?
The great food transformation refers to a global shift toward sustainable food systems. For survivalists, it’s about adopting practices that ensure a secure food supply without compromising environmental sustainability. This includes growing climate-friendly food, reducing reliance on high-food-miles products, and making sustainable food choices every day.
10. How Can I Make More Sustainable Food Choices Today?
Start small and focus on practical, sustainable options like:
- Supporting local organic farmers.
- Reducing food waste by preserving leftovers and composting scraps.
- Choosing environmentally-friendly foods over highly processed options.
By integrating sustainable farming practices and reducing your reliance on food manufacturers, you contribute to a sustainable food future for yourself and the planet.
Final Takeaway
Sustainable food sources are the backbone of long-term survival. By growing, hunting, and making sustainable food choices, you secure your food supply, reduce your foodprint, and align with environmental sustainability.
The question isn’t if you’ll need these skills. It’s when. And when that time comes, will you be ready?

